Generating
a Rectangle Grid
The rectangle or
regular grid
is a digital model that shape surfaces through rectangle face
polyhedron. Vertexes of those polyhedra can be the sampled points in
case they have been acquired in same XY locations that define the
wanted grid.
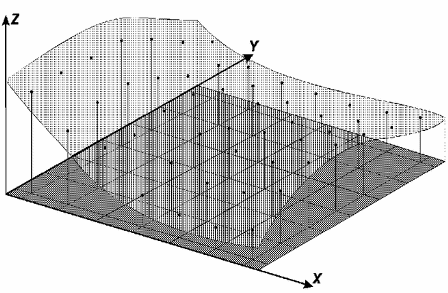
The
rectangle grid
generation must be done when a sampled data in the surface is not
obtained with regular spacing. Thus from isoline contained information
or in sampled points it is generated a grid that represent as closest
as possible to the real surface. Initial values to be determined are x
and y coordinate space in a way they can represent close values to the
grid points in big variation regions. At same time, they should reduce
redundancies in almost plane regions.
The grid space,
i.e. x and y
resolution, should be ideally lower or equal to the lower distance
between two samples in different quotas. When generating a very thin
grid (dense), with a very small distance between points, there will be
a bigger amount of information about the analyzed surface, but will
need more time to generate. Otherwise considering big distances among
points, it will be created a thick grid that could lose information.
Therefore, the final grid resolution must have a commitment of data
accuracy and grid generation time.
Once defined the
resolution
and consequently the coordinate in each grid point, it is possible to
apply one of interpolation methods to calculate the elevation rounded
value.
The regular grid
can be generated from samples, isolines, regular grid or irregular grid.
In the case of
samples and isolines the following interpolators can be used:
- nearest neighbor
- simple mean
- weighted average
- weighted average per quadrant
- weighted average per dimension and quadrant
- bilinear spline
- bicubic spline
- mitasova spline
In
order to generate a new regular grid from other regular grid the
following interpolators can be used:
For the
generation of rectangular grid from a TIN ("Triangular Irregular
Network") tthe
following interpolators can be used:
- linear
- quintic without breaklines
- quintic with breaklines
It is
accessible through:
PROCESSING → DTM
PROCESSING
→ DTM GENERATION...
1.
Select the type of input layer.
- Isolines/Samples:
one can select a layer of each type or only one.
2. Use combobox or

to select a isolines
and/or samples layer. If you are not going to use both types of layer
leave one blank, but one type should be selected.
If the selected layer does not have 3d information in its geometry, in
the
Quota Column
combobox, select the attribute that contains the attribute to be used.
- Grid
Retangular/Triangular, only one layer can be selected.
2. Use combobox or

to select a grid
retangular or triangular layer.
In the case of rectangular grid it is possible to set the dummy value
of this.
3. Select the
interpolator:
- nearest
neighbor
- simple mean
3.1. Set the Radius value:
Maximum radius used to filter elements. Default value is calculated
using box of input layer.
- weighted average
- weighted average per
quadrant
- weighted average per
dimension and quadrant
3.1. Set the Power :
power value used in the IDW interpolator.
3.2. Inform the Radius :
Maximum radius used to filter elements. Default value is calculated
using input layer box.
- bilinear spline
- bicubic spline
3.1. Set Separation in X / Y:
are the number of parts considered in the x and y directions.
3.2. Set Minimum Points: the
minimum of points considered.
3.3. Set Overlapping:
overlap value considered.
3.1. Set Tension: the
tension spline factor considered in the spline fitting process.
3.2. Set Smothness: the
smooth factor used.
3.3. Set Minimum Points: the
minimum of points considered.
- bilinear
- bicubic
- linear
- quintic without breaklines
- quintic with breaklines
4. Inform
Output Parameters
Resolution X / Y :
grid space.
Dimension C / L
: number of lines and columns.
Note that these values are calculated as they are edited, when
entering resolution the size of the grid is calculated and vice versa.
5. Set
Output SRS

to select output layer SRS.
6.
Inform the Output Repository
by clicking on:
6.1.

to select the output
directory
and also inform the new layer name to store the result, or
6.2. 
to select
the Data Source
and Inform
the new
Layer
Name to store the aggregation result.
7. Click OK
to perform the
operation or Cancel to close the interface.

